买卖股票问题
Leetcode 121 - 123 是三个简单的股票买卖问题。都可以用O(n)的时间复杂度求解。
121 最简单
Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i.
If you were only permitted to complete at most one transaction (ie, buy one and sell one share of the stock), design an algorithm to find the maximum profit.
Example:
Input: [7, 1, 5, 3, 6, 4]
Output: 5
解法也比较直接,一次遍历可以完成。
1 | var maxProfit = function(prices) { |
122:
Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i.
Design an algorithm to find the maximum profit. You may complete as many transactions as you like (ie, buy one and sell one share of the stock multiple times). However, you may not engage in multiple transactions at the same time (ie, you must sell the stock before you buy again).
可以证明交易的方法一定是连续的子序列可以得到更优的利润,因为题目有条件不限制交易次数。
如果不连续比如[1 2 5 3 9] 中的[1 2 5 9],那么一定有[1 2 5]和[3 9]的交易方法优于不连续的子序列[1 2 5 3 9]。
而且对于一个递增子序列,首尾相减获得的利润差一定为每一段两项的利润差之和。
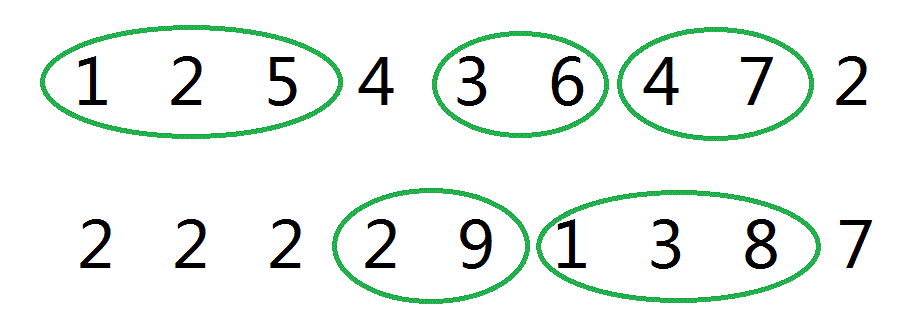
1 | var maxProfit = function(prices) { |
123:
Design an algorithm to find the maximum profit. You may complete at most two transactions.
这题需要借助双向扫描的思想,首先从头到尾,并计算d[i]=max{d[i-1], prices[i] - min},表示的含义是从第0时间点的股价,到第i时间点的股价,进行一次交易的最优的利润是多少。
再从尾扫到头,并计算d2[i]=max{d2[i+1], max - prices[i]}, 表示从第i时间点的股价,到最末时间的股价,进行一次交易的最优利润。
然后求出最大的d[i]+d2[i],为本题解,其中d[len-1]+d2[0]如果为最大值,则表明进行一次交易即可获得最大值。
1 | var maxProfit = function(prices) { |
如果问题继续进行升级,那么恐怕需要O(n^2)复杂度的动态规划算法了。
补充: 今天又看到了升级版
Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i.
Design an algorithm to find the maximum profit. You may complete at most k transactions.
首先计算各项之间的差值。
DP解法申请两个数组
L[k][i] 表示以i结尾进行k次交易的最小值,最后一次交易必须以i结尾。
G[k][i] 表示以i结尾进行k次交易的最小值
L[k][i] = max { L[k][i-1] + d[i], G[k-1][i-1] + d[i] } G[k][i] = max { G[k][i-1], L[k][i] }
如果k >= n/2, 则调用贪心算法,因为对于每一个数列的最大交易次数是n/2
1 | var maxProfit = function(k, prices) { |
继续补充,今天又看到了冷冻期版本
Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i.
Design an algorithm to find the maximum profit. You may complete as many transactions as you like (ie, buy one and sell one share of the stock multiple times) with the following restrictions:
You may not engage in multiple transactions at the same time (ie, you must sell the stock before you buy again).
After you sell your stock, you cannot buy stock on next day. (ie, cooldown 1 day)
Example:
prices = [1, 2, 3, 0, 2]
maxProfit = 3
transactions = [buy, sell, cooldown, buy, sell]
借助上题的解决方案,使用全局数组g[]表示全局最小和局部数组l[]表示以i交易为最后一个交易的局部最小(也就是说在i点出售股票)
递推式l[i] = max{l[i-1], g[i-3](0 if i<3)} + price[i] - price[i-1]g[i] = max{g[i-1], l[i]}
1 | class Solution { |
在discussion area又看到了一个有趣的解法,状态机解法,因为是求无限量交易的最优解,所以这种方法成立。
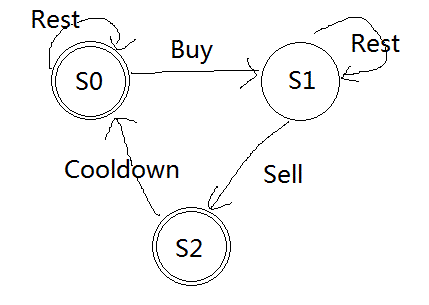
状态转移s0[i] = max{s0[i-1], s2[i-1]}s1[i] = max{s1[i-1], s0[i-1] - prices[i]}s2[i] = s1[i-1] + prices[i]
初始状态s0[0]=0s1[0]=-prices[0]s2[0]=INT_MIN
1 | class Solution { |
同时,由于每一个状态仅仅依赖于上一个状态,所以可以把空间也优化为O(1)。