这个简单的Java程序竟然有问题,如果我们输入的是中文,程序不会正常输出。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = scanner.next();
System.out.println("你输入了 = "+ s);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
| 结果:
run:
陶
你输入了 = ��
成功生成(总时间:7 秒)
|
这究竟是为什么呢?
先了解一下Java的输入文件流机制,System.in是字节流。系统是按照每个字节读入,最后组成字节组作为读入的。
Scanner是套在System.in外面的字符流。下面我们直接显示System.in读入的字节
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public class ChineseEncoding {
private static void printBytes(byte[] bytes) {
for (byte b : bytes) {
printByte(b);
}
System.out.println();
}
private static void printByte(byte abyte) {
String hex = "00"+Integer.toHexString((int)abyte);
System.out.print(hex.substring(hex.length() - 2) + "\t");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String s = "陶";
printBytes(s.getBytes("GBK"));
printBytes(s.getBytes("UTF-8"));
byte b = (byte) System.in.read();
while (true) {
printByte(b);
b = (byte) System.in.read();
}
}
}
|
我们可以看到System.in读入的字节流是默认以GBK编码的。
1
2
3
4
5
| run:
cc d5
e9 99 b6
陶
cc d5 0a
|
对比,可以知道Scanner的字符套默认是以GBK编码转化的。
下面这个输出可以验证
1
2
| byte[] b = new byte[]{new Byte((byte) 0xcc), new Byte((byte) 0xd5)};
System.out.println(new String(b, "GBK"));
|
这个输出可以准确输出为:陶。
因此,我们有两个方法解决这个问题:
一、使用以下方式读入
1
| Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in, "GBK");
|
二、更改默认编码
1
2
| String encoding = System.getProperty("file.encoding");
System.out.println(encoding);
|
这个输出为UTF8。如果输出为GBK则不会有开头所提的问题。可以认为file.encoding的值是Java程序main入口函数的默认编码。
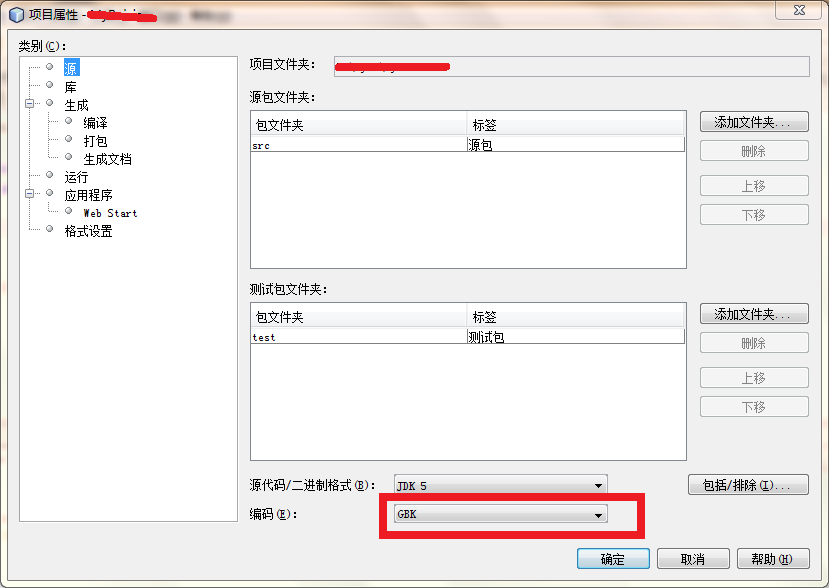
NetBeans修改方法如下:
附注:
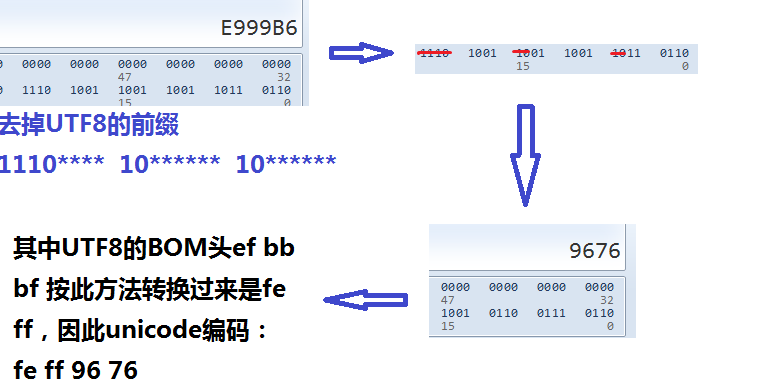
可以看到陶的UTF8编码为
e9 99 b6
ef bb bf e9 99 b6(带有BOM头,其中BOM头为ef bb bf)
Unicode的编码为fe ff 76 96,其中fffe是控制高位和低位的发送顺序的。
其中变化方法如下: